A material long used by men

Wood has always been favored for construction, furnishing, or for insulation or heating. Mulberry bark was used for paper by the Chinese. Also, wood always had an important place in art.

Wood is an essential material in architecture, used in every type of construction from parquet floor to framework. Houses and buildings are always more or less made of wood, as well as pieces of furniture, boats, musical instruments...
Wood is used so much because it has many benefits : robust, insulating, durable, ecological thanks to sustainably managed forests, also pleasant to use. Moreso, some problem inherent to its use have now been counteracted : for instance, wood-eating organisms are now disposed of with specific products.
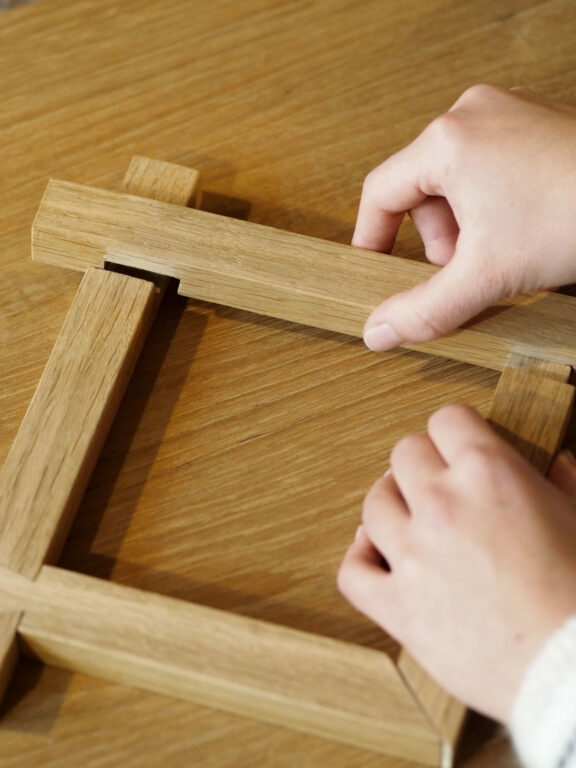
The cabinetmaker and the carpenter don’t work the same way. The carpenter makes pieces of furniture or solid wood structures, while the cabinetmaker, after having built a wood structure, covers it with a thin layer of fine wood, called veneer. The cabinetmaker ths has to pay attention to the different natures and shapes of wood all throughout the process of creation.
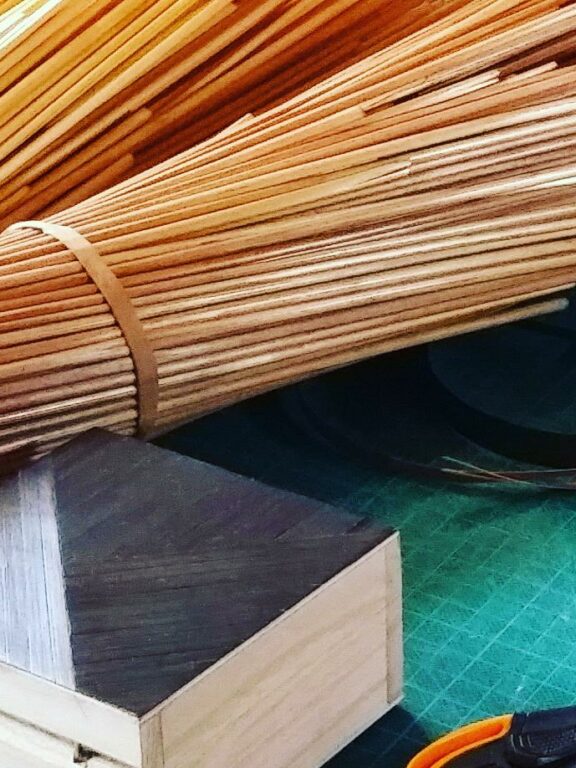
Marquetry is another wood art, it’s a decor the marquetry cabinetmaker builds from veneer, after a drawing, in order to give them a particular shape. He then assembles them, forming a whole that will be pasted on a support, like a painting or a piece of furniture.
That art developed especially during the Trecento in Italia, then was used a lot for Louis XIV and Louis XV style furniture.
The different types of wood
Based on the weather, different trees develop and generate different types of wood. With a temperate climate, we will have conifers such as pine, and fir, or hardwood such as aspen or birch. Some, like fruit trees, among others, are not grown for their wood, like cherry for example, but they can still be useful in cabinetmaking and marquetry.

- Types of wood specific to certain uses :
The most common types of wood
Oak is the traditional type of wood for framework, along with chestnut and spruce, for they don’t rot. Oak was also used a lot in naval construction.
Charm and maple are very useful for heating, because they produce more heat per cubic meter than most types.
Cabinetmaking types of wood
Cherry is a light brown wood that can replace mahogany, and is used to make solid furniture in carpentry, as well as veneering.
Walnut is a low density, colorful and veined wood, favored for veneering.
Maple is a very light, almost white wood, and one of the most favored type for cabinetmakers.
Plane tree is a light, solid and moisture resistant type, although a bit dificult to use sometimes.
Fir is a light and quite solid wood, used for solid furniture, and also for parquet floors and stairs.
Exotic wood, such as mahogany, ebony, yew and lemon tree, is especially used in marquetry[:] Read more…
 tury invention, it is a binder that hardens under the action of water, today most often used in the manufacture of reinforced concrete, or mortar.
tury invention, it is a binder that hardens under the action of water, today most often used in the manufacture of reinforced concrete, or mortar.